
HOMER Pro 3.15

![]()
Important: The Thermal Load Controller is part of the Combined Heat and Power module. See Adding Modules for more information on purchasing modules.
The Thermal Load Controller page contains the cost and size inputs for a thermal load controller. The Thermal Load Controller allows excess electrical production to serve loads on the thermal bus. A thermal load controller is not required for systems with a thermal load but without it, excess electrical production is not used.
Costs
The Costs table includes the initial capital cost and replacement cost, as well as annual operation and maintenance (O&M) costs. The table also includes the size (kW) corresponding to the costs in each row. When specifying the capital and replacement costs, be sure to account for all costs associated with the thermal load controller, including installation.
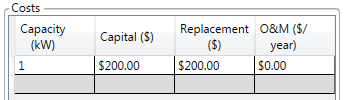
Note: The capital cost is the initial purchase price, the replacement cost is the cost of replacing the thermal load controller at the end of its lifetime, and the O&M cost is the annual cost of operating and maintaining the thermal load controller.
Click the Click here to enter new item option to enter additional rows in the Costs table to account for changing costs with scale.
Size
Enter the capacities you want Homer to consider for the optimal system in the Capacity Optimization table.
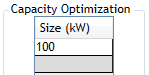
HOMER uses the information you enter in the Costs table to calculate the costs of each size, interpolating and extrapolating as necessary. You can see the results in the Cost Curve graph.
Other Inputs
|
Variable |
Description |
|
Lifetime |
The service life in years of the thermal load controller |
|
Bus Connection |
Specify AC, DC, or Both for the buses from which excess electrical production can be drawn |
|
Do not include the thermal load controller in the optimization |
This option models the thermal load controller with infinite capacity and no cost. |
Note: To the right of each numerical input is a
sensitivity button ( ) that allows you to do a sensitivity analysis on that variable. For more
information, see Why Would I Do a
Sensitivity Analysis?
) that allows you to do a sensitivity analysis on that variable. For more
information, see Why Would I Do a
Sensitivity Analysis?
See also
