
The Storage section allows you to enter the cost and sizing you want HOMER Front to consider as it searches for the optimal system.
Sizing
Select the storage type in the drop-down menu; this selection determines the number of MW and MWh per unit. The sizing entry allows you to test different numbers of units of these modules. For example, you may enter 100 units of 1MW/4MWh modules for a total system size of 100MW/400MWh. Enter multiple sizing options to test which configuration may lead to the best economics.
Click on Add another storage technology to add another storage option. HOMER simulates each of the storage types, one component at a time. You can add more than one storage component to the model, but each one must include a zero in the Sizing option.
Costs
There are two ways to include your equipment cost information.
•Select the Price Sensitivity Analysis to enter a single value or to consider different values over the project lifetime.
•Select the Cost Breakdown option to include detailed cost information by line item.
Price Sensitivity Analysis
Price Sensitivity Analysis is the total installed costs for storage. Include every cost related to storage in this entry. You may assign a sensitivity (different values) to this parameter
The cost table includes the initial capital cost and augmentation per storage item, as well as annual OPEX costs per storage. When specifying the capital and replacement costs, be sure to account for all costs associated with the storage, including installation. You may specify storage Converter costs in the storage section or choose to include them in the Storage DC/DC Converter.
Note: The Capital cost is the initial purchase price. The Replacement cost is the cost of replacing the storage at the end of its lifetime. The OPEX cost is the annual cost of operating and maintaining the storage.
Note: Below each numerical input is a sensitivity button ( ) that allows you to do a sensitivity analysis on that variable. For more information, see Why Would I Do a Sensitivity Analysis?
) that allows you to do a sensitivity analysis on that variable. For more information, see Why Would I Do a Sensitivity Analysis?
Cost Breakdown
Cost Breakdown allows you to specify different line items with different units.
The Detailed Cost Structure includes:
•Direct Capital
•Indirect Capital
•Annual Operations and Maintenance Costs (OPEX)
•Major Replacement Costs
You can select the Add New Button to add an additional cost item to each section. Select the appropriate units ($, % direct, or $/Wdc) in the associated drop-down menu. The Cost Breakdown includes suggested costs and can be edited.
Augmentation ($/unit)
This field is cost per kWh storage capacity that incurs when the battery reaches the augmentation degradation limit.
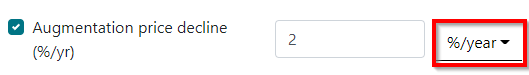
Augmentation Price Decline
Augmentation price decline captures the changing cost of storage in the future. The ‘%/year’ price decline input allows you to specify a year-over-year change in the price for augmenting, starting with the price specified in Augmentation ($/unit).
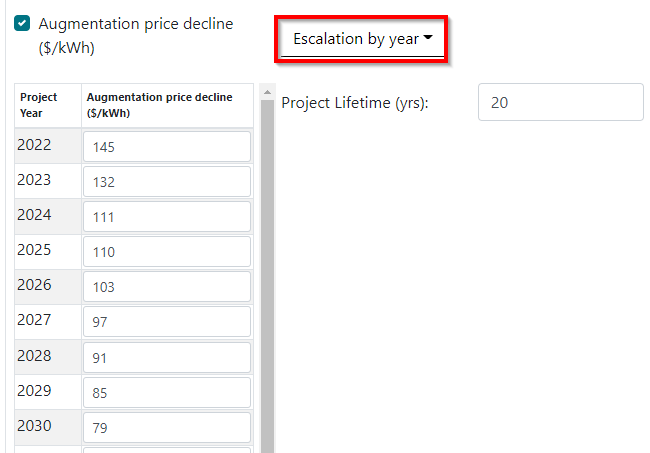
The ‘Escalation by year’ option allows the user to specify a price change for each year, on Jan 1st of the specified year. The Augmentation price will be interpolated based on what day of the year the augmentation takes place.
Augmentation degradation limit
This limit refers to the point at which the battery will be augmented. Ex: If you set your limit to 10%, the battery will be augmented when it reaches 90% capacity.
Note: Below each numerical input is a sensitivity button ( ) that allows you to do a sensitivity analysis on that variable. For more information, see Why Would I Do a Sensitivity Analysis?
) that allows you to do a sensitivity analysis on that variable. For more information, see Why Would I Do a Sensitivity Analysis?
Constant Degradation
You can define a degradation that depends on time as opposed to cycling.
See Also